What is a crypto wallet?
Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic security.
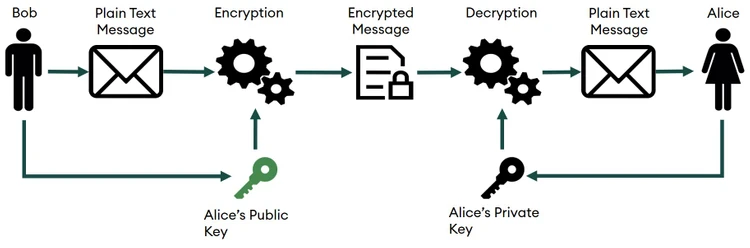
Owning something on the blockchain means you control the private cryptographic key to a public address, or wallet, where your tokens, both fungible and non-fungible are held.
Source: SEBA Research
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallet
A crypto wallet is a software program or physical device that allows you to store your crypto and allow for the sending and receiving of crypto transactions.
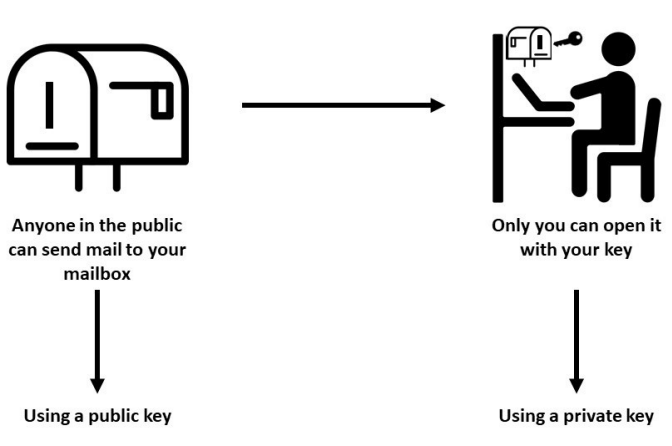
Public address
Anyone can see your public address and send tokens to it, just like a real address.
But only you can interact with the tokens in your wallet by signing transactions with your cryptographic key.
Wallets are different for each blockchain, so when you’re buying NFTs on the Ethereum network, you’re using an ETH wallet with an ETH address, formatted 0x#### which is why you see social media accounts like 0xmat, 0xjessica, etc. The ETH or NFT you receive will be sent to this address.
Types of crypto wallets
1. Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are basically wallets that connect to the internet and generally offer lesser security. They offer better accessibility due to their connection with the internet. Even if hot wallets are vulnerable to fraudsters and hacker attacks, they are highly user-friendly. Examples are Coinbase and Blockchain.info.
2. Cold Wallets
Cold wallets are digital offline wallets where the transactions are signed offline and then disclosed online. They are not maintained in the cloud on the internet; they are maintained offline to have high security. Examples are Trezor and Ledger.
3. Custodial Wallets
A custodial wallet is intermediated by a third party. It is a wallet solution where a third party holds the private keys for you. This effectively means that it's not you but another party who controls the private keys to the crypto assets on your wallet. This other party can either be an exchange, a broker, or a (crypto) bank. You cannot use these wallets to buy NFTs, only for cryptocurrencies.
Custodial wallet, hot wallet, or cold wallet? Most crypto users use all of them, but it all depends on your needs.
Topics
Recent comments
